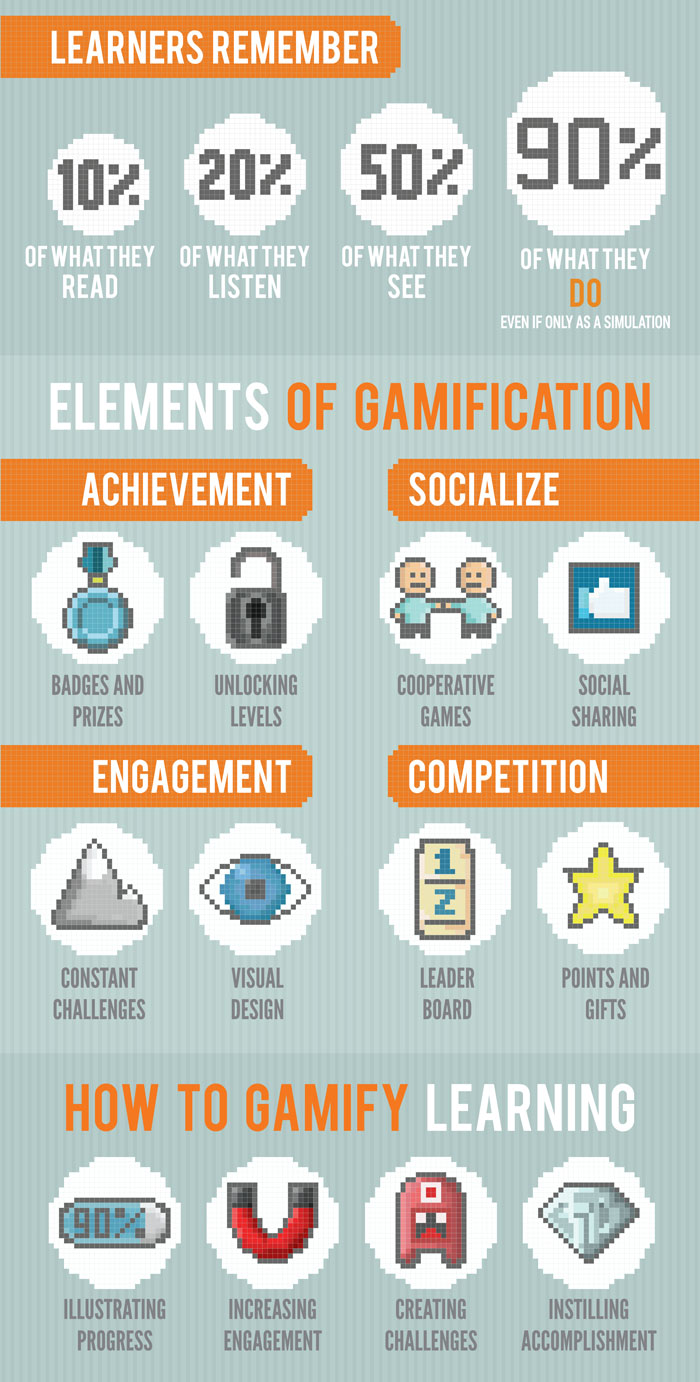
A 2013 study by the American Psychological Association highlights the cognitive, motivational, emotional, and social impact games can have on human behavior. A number of organizations are using gamification to train workers, educate students, solve problems, and generate new ideas and concepts. These organizations range from business schools to software companies, to governmebt organizations and beyond. In almost every industry it is possible to find an example of the gamification of learning, innovation and problem solving.


The use of game-based mechanics, aesthetics and game thinking to engage people, motivate action, promote learning, and solve problems.
Game designer Jane McGonigal, in a recent Ted Talk, explained how game mechanics can be leveraged to tackle the problems of poverty, hunger, climate change, global conflict and more. Her reason for wanting to tap into gaming as a solution is compelling.
When we play a game, we tackle tough challenges with more creativity, more determination, and more optimism, and we are more likely to reach out to others for help
Learning and development professionals must understand the growing trend of applying game-based techniques to the development of instruction through creating time-based activities, leveling up of learning experiences, storytelling and other techniques. This is also crucial because traditional methods of learning are losing favor, time and attention of learners is limited, and learning professionals must focus on providing engaging and goal-oriented solutions by matching game strategies with the different types of learning content.